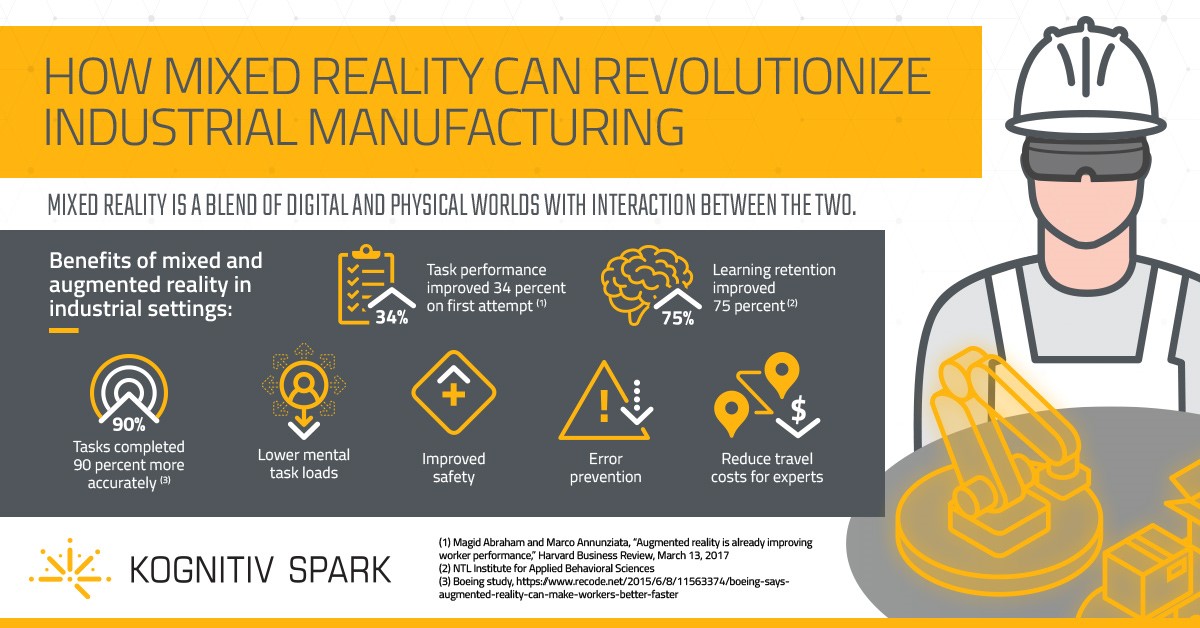
Boeing reduced their aircraft manufacturing time by over 25% and lowered error rates to nearly 0% by equipping their production lines with AR-based technology!
Augmented Reality (AR) is increasingly becoming a technology to reckon with in several industries and sectors, more so in the manufacturing sector. Every stage of the production or manufacturing process, beginning from research and product development to end-of-life management, is reaping the benefits of a melange of AR offerings that bolster the manufacturing process.

Why AR in Manufacturing?
‘If you want to see your product in the environment it will be used in, AR can do that for you faster, and less expensively than building a prototype’ – Matt Huybrecht.
Hard-ware based products are increasingly being manufactured through cutting-edge technological processes that leave little to no room for error. Organisations across the globe need to ensure that quality is preserved to stay ahead, or at least on par with the competition.
AR bridges the gaps in technology that can potentially lead to errors, and results in quality production, optimised planning, quicker turnaround, lesser wastage, and a host of other tangible and intangible benefits. Augray has enabled hundreds of organisations to enhance and improve their end-to-end manufacturing processes by enabling AR-based technologies. Here is a sneak peek into what AR can do for your business.


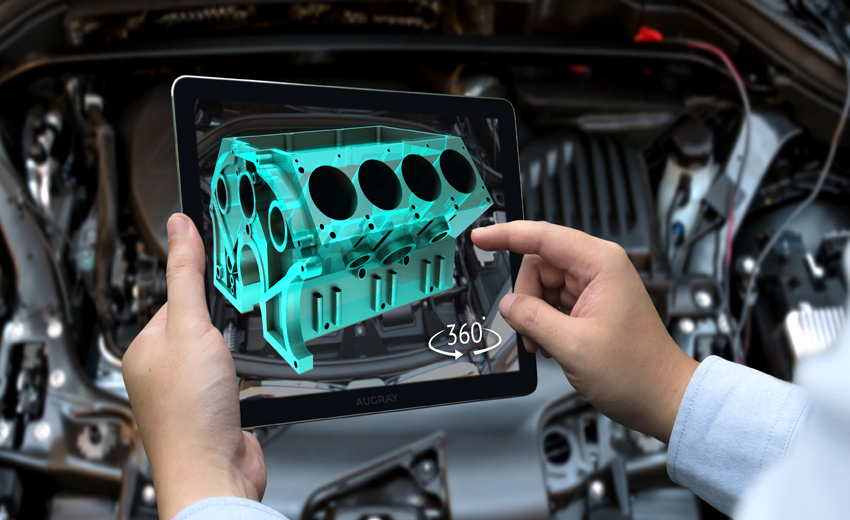
Visualisation and Prototyping
creating multiple prototypes for the purpose of visualisation and functionality testing of often expensive, labour intensive, and time consuming. AR makes this process of visualisation extremely efficient with respect to economics and labour. By creating a digital twin or a virtual model, engineers, designers, and product developers can visualise the product without having to build a physical prototype. This considerably reduces the time spent in design and development and subsequently shortens the time the product takes to reach the market. With the power of AR, products can be translated from the drawing board to visual and even physical prototypes (through rapid prototyping or 3D printing) within days or weeks instead of months.
Complex Assembly
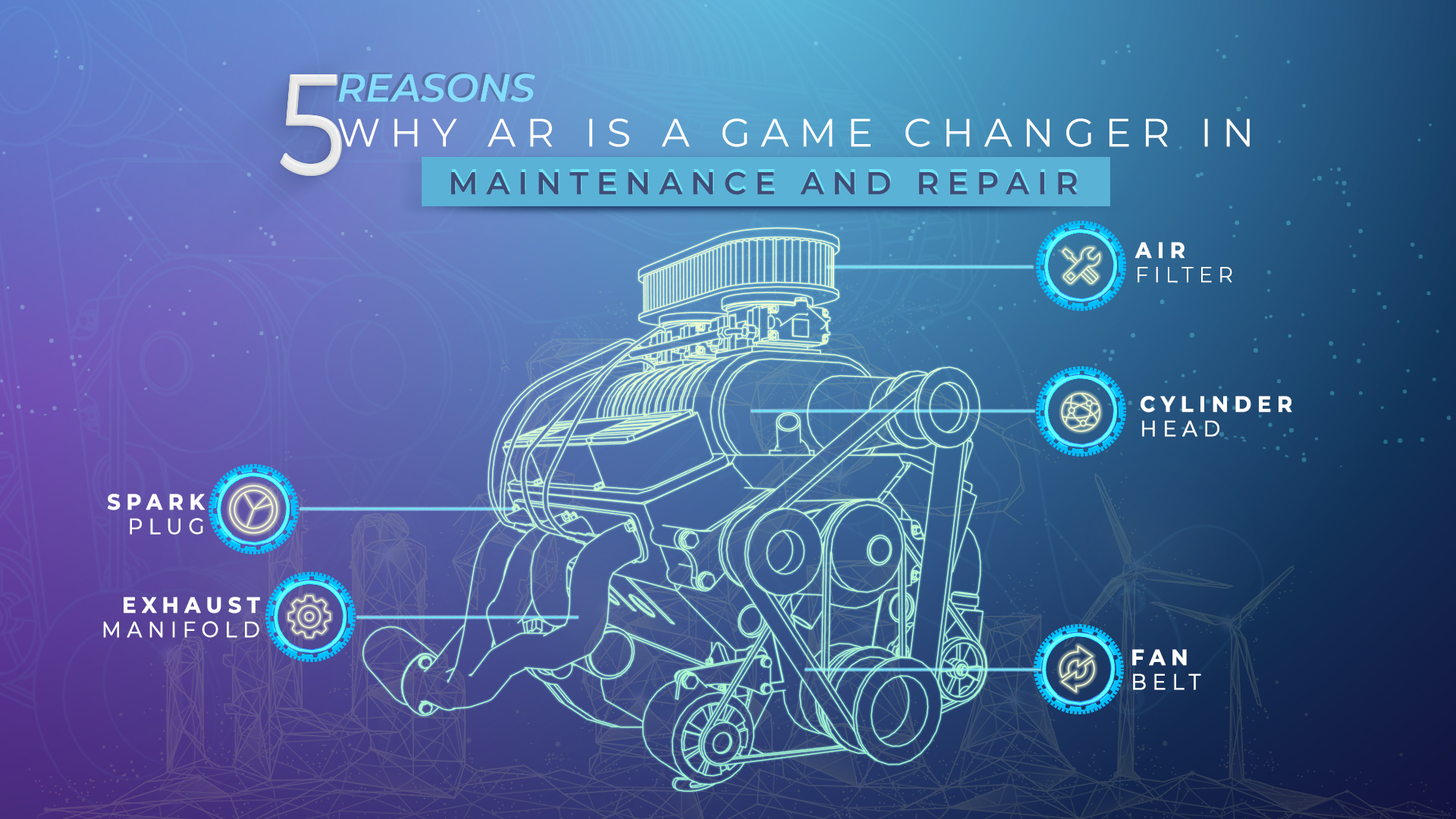
Every large machine requires hundred if not thousands of parts to be assembled with utmost accuracy and precision. In the case of aircraft, ships, large automobiles, and power generation machinery, tens of thousands of components need to be assembled, and the wafter thin error margin literally leaves no room for errors. In such a scenario, manual assembly and inspection would require the expertise of multiple technicians to ensure that precision. However, when the process is enabled with AR, the makes the process of assembly skill agnostic and ensures that all components are fitted in accordance with requirements and norms.
For instance, aircraft companies and automotive manufacturers now use AR-enabled goggles to ensure that seats are fitted in the right place. When these devices are used, an alarm is raised even if the technician deviates the positioning by a millimetre. This ensures that the technician does not waste time in refitting seats by ensuring that they are assembled the correct way at the first instance.
Supply Chain and Logistics
Small and medium scale establishments that do not have a separate division for procurement and stock-taking more often than not find themselves in a soup when they require a particular component but find it short in supply. On the other hand, in the case of fast-moving goods, organisations often find they have ingredients or perishable components in excess and stand to lose if these constituents are not processed at the right time. AR-enabled organisations can simulate the process and predict machine failure, downtime, and shortage of demand. This enables the organisation to plan the supply chain, enabling the organisation to optimise machine run time, minimise wastage, reduce manufacturing lead time and most importantly, achieve shorter sales processes.
Product Life Cycle Management
The entire product life cycle can be simulated using AR. Multiple-use cases can be modelled to test the efficacy and life of the product, enabling organisations to play the end-of-life of the product even before the product actually hits the market. Additionally, with the combination of AR and 3D printing, organisations need not even produce spare parts for retired products in the long run. Users can purchase, retrospectively modify, or even reverse engineer parts to suit their needs long after an organisation has stopped producing a product. This opens up a new space in which organisations can monetise their offerings while simultaneously catering to the needs of the customers.
AR in every step of Manufacturing
The novel, cutting edge AR-based technologies are undoubtedly changing the face of modern era manufacturing by making processes swifter, more sustainable and efficient. Augray has borne witness to this paradigm change in Industry 4.0.
The possibilities that AR offers in enhancing Manufacturing is immense and boundless. Necessity, the mother of invention, has made it mandatory for organisations to embrace this change of offer the best value for themselves and all their stakeholders.
Users get interacted with Augmented reality (AR) technology. Enhance the real-world environment by superimposing digital data or virtual objects. There are many applications for AR, but the four main ones are covered below:
Entertainment: AR is frequently employed in the entertainment sector to give people immersive experiences in everything from video games to movies. While AR movies like Iron Man 2 and Avatar have shown the technology’s promise, AR apps like Pokemon Go and Ingress have gained widespread popularity.
Education: To create interactive learning experiences. Students are given a better comprehension of complex ideas using AR-enabled textbooks, applications, and simulations, which also aid in real-time information visualization. Augmented reality is also employed in education.
Retail: AR is revolutionizing the retail sector by enabling shoppers to virtually try on clothing, picture furniture in their homes, and even preview things before purchasing. AR also gives shops a chance to present their goods in unique and engaging ways to enhance engagement and sales.
Industrial: To increase production, cut down on errors, and improve worker safety, AR is being employed in industrial settings. Workers may access real-time information, like schematics and instructions, through AR-enabled devices, enabling them to finish tasks swiftly and precisely. Moreover, AR is applied to maintenance and repair tasks, giving staff members a hands-free, heads-up display of crucial information.
The usage of augmented reality (AR) technology is in many different industries. Let’s check it below!
Gaming: Augmented reality (AR) has completely changed the gaming business. Because consumers can play games in a more realistic way with virtual things. That is superimposed on the actual world.
Education: Augmented reality technology is employed in classrooms to give students meaningful and interesting learning experiences. AR can be used, for instance, to show 3D models of items or to recreate historical events vividly.
Medical: AR technology is utilized in safe and controlled medical training environments to imitate surgical and other medical procedures.
Architecture and engineering: Virtual models of buildings and structures are created using augmented reality (AR) technology in architecture and engineering, enabling designers to see and test ideas before construction.
Tourism: Virtual tours and immersive encounters of landmarks, museums, and other attractions are made possible with augmented reality (AR).
Military: Real-time surroundings information can be sent to the soldiers in a form of augmented reality . it include enemy positions and terrain data,
Ultimately, AR has the power to disrupt a wide range of industries and open up new commercial and personal opportunities.
Augmented reality often comes in four flavors:
Marker-based AR: This kind of AR overlays augmented content on top of a visual marker, like a QR code or image, to make it more visible.
Markerless AR, often called location-based or position-based AR locates the user and their orientation using the device’s GPS, accelerometer, and digital compass to overlay content in the real environment.
AR that projects digital images onto actual surfaces, including walls or tables, gives the impression that the augmented content interacts with the real world.
AR that uses superimposition substitutes real-world objects with virtual counterparts to provide the impression that the virtual object is physically there. Video games and the entertainment industries both frequently use this kind of AR.
Pokemon Go is a famous augmented reality (AR) application. It’s a smartphone game with augmented reality (AR) technology. let users use their mobile devices to catch fictional animals (Pokemon) in the real world. Since being released in 2016, Pokemon Go has quickly gained enormous popularity.
This game has downloaded more than billion times. Snapchat, Instagram, and Google Translate are well-known AR programs. That use the technology to enhance real-world photos and videos with translations, effects, and filters.
Augmented reality (AR) uses the camera and display of a mobile smartphone to create a illusions of digital data in a actual world. Although artificial reality (AR) can use some AI-related methods and algorithms, this does not mean it is AI.
Similar to some AI applications, augmented reality frequently uses computer vision algorithms to recognize and monitor actual physical objects or surfaces in real time.
Not important to simulating human-like intelligence or decision-making. The main goal of AR is to improve the user’s view and interaction with the real environment.
AR can undoubtedly benefit from the use of AI to enhance its capabilities. For instance, the identification of objects in the user’s environment using AI-powered picture recognition could lead to the provision of more precise or pertinent AR overlays.